Body Mass Index or BMI Calculator is a popular tool to understand a person’s health status by measuring his healthy body weight relative to his height. BMI calculators are essential for Health Awareness and to achieve fitness goals. This tool is also known as: ideal weight calculator, BMI health calculator, Body Mass Index calculator etc.
BMI Calculator
How to Use the BMI Calculator
- Gender Selection: Select from a “Male or Female” option.
- Enter your height in centimeters (cm).
- Enter your weight in kilograms (kg).
- Click the “Calculate BMI” button.
- The tool will display your BMI score as a slider with color coded ranges as follows:
-
- Underweight (16–18.5): Red to Orange
- Normal (18.5–25): Green
- Overweight (25–30): Yellow
- Obesity Class I (30–35): Pale Red
- Obesity Class II (35–40): Dark Red
- Obesity Class III (40–50): Deepest Red
Advantage of This Tool:
- Advanced Features: Gender selection and detailed BMI categories.
- Visual Appeal: Color-coded slider for easy understanding.
- Responsive Design: Works seamlessly on all devices.
- User-Friendly: Simple and intuitive interface.
What Is BMI?
The Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator helps estimate whether your weight is healthy for your height and age.
BMI is a simple measure that relates weight to height to assess body fat levels. It is widely used to classify individuals as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. While BMI does not measure body fat directly, it is a reliable screening tool to identify potential health risks and determine whether further evaluation is needed.
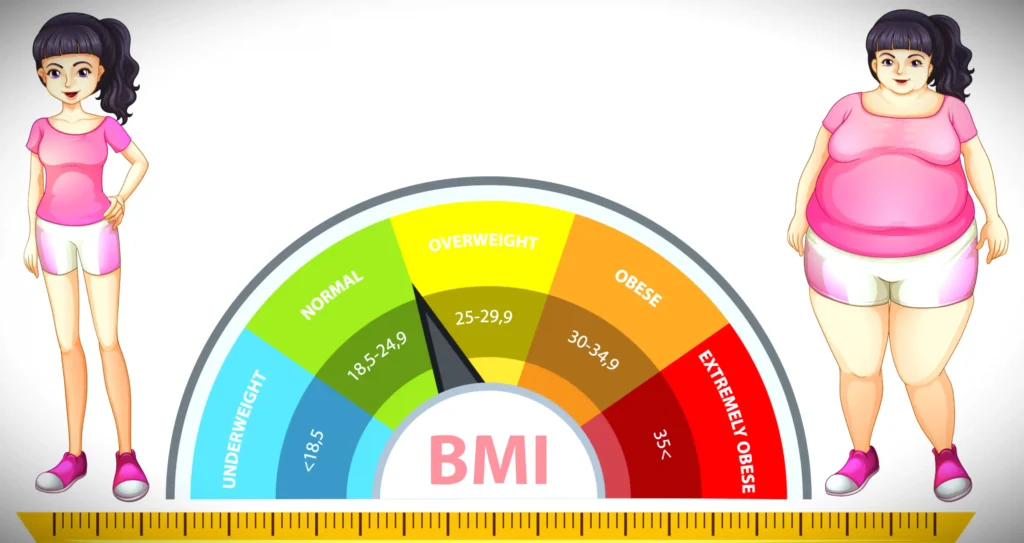
BMI Categories for Adults (WHO)
- Underweight: Below 18.5
- Normal: 18.5 – 24.9
- Overweight: 25 – 29.9
- Obese: 30 and above
(BMI standards apply to adults aged 20+.)
BMI for Children and Teens (CDC)
For ages 2–20, BMI is assessed using percentiles:
- Underweight: Below 5th percentile
- Healthy weight: 5th – 85th percentile
- Overweight: 85th – 95th percentile
- Obese: Above 95th percentile
This accounts for growth and development differences.
Health Risks Linked to BMI
Being Overweight May Increase Risk Of:
- High blood pressure and cholesterol
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease and stroke
- Joint problems and sleep apnea
- Certain cancers
- Reduced quality of life
Being Underweight May Lead To:
- Nutritional deficiencies and anemia
- Weak bones (osteoporosis)
- Low immunity
- Hormonal and fertility issues
- Higher surgical and mortality risks
Maintaining a BMI below 25 is generally recommended, but individual health advice should always come from a medical professional.
Limitations of BMI
BMI does not account for:
- Muscle mass
- Bone density
- Fat distribution
- Age, sex, or ethnicity
Athletes or muscular individuals may have a high BMI but low body fat, while older adults may have normal BMI with higher fat levels. BMI works best when used alongside other health measurements.
BMI Formula
- Metric:
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height² (m²) - US Units:
BMI = 703 × weight (lb) ÷ height² (in²)
BMI Prime
BMI Prime compares your BMI to the upper healthy limit (25):
- BMI Prime = BMI ÷ 25
A value:
- Below 1 → Healthy or underweight
- Above 1 → Overweight or obese
It helps compare BMI across populations and regions.
Ponderal Index (PI)
The Ponderal Index is similar to BMI but uses height³ instead of height². It is more accurate for very tall or very short individuals, where BMI can be misleading.
- Metric:
PI = weight (kg) ÷ height³ (m³) - US Units:
PI = height (in) ÷ ∛weight (lb)
Conclusion
BMI is a practical and widely accepted health indicator for most people. While not perfect, it provides a valuable first step toward understanding weight-related health risks when combined with other assessments.
Disclaimer: This tool is for information purpose only and it should not be considered as medical advice. Please consult your physician for medical advice.
